In our digital lives, file extensions play a crucial role. They help us identify file types, determine which programs can open them, and enhance our overall operating system (OS) experience.
By default, Windows conceals these file extensions to simplify the user interface. However, there may be instances where viewing these extensions becomes necessary, especially for tasks involving file management, software development, or cybersecurity.
In this SEO-optimized guide, we will demonstrate how to display file extensions in Windows 7, Windows 10, and the new Windows 11 using built-in options, registry edits, and PowerShell commands.
Contents
- 1 What are File Extensions?
- 2 Importance of Showing File Extensions in Windows 10:
- 3 Displaying File Extensions in Windows 10 and Windows 11
- 4 Showing File Extensions in Windows 7
- 5 Displaying File Extensions via Registry Editor
- 6 Using PowerShell to Show File Extensions
- 7 Understanding File Extensions
- 8 10 frequently asked questions (FAQ) related to Windows 10:
- 9 Conclusion
What are File Extensions?
File extensions are suffixes appended to filenames, separated by a dot, indicating the format or type of the file. For example, “.txt” denotes a text file, “.jpg” indicates an image file in JPEG format, and “.docx” represents a Microsoft Word document.
File extensions serve as identifiers, allowing the operating system and associated applications to recognize and process files accordingly.
Read Also:
Importance of Showing File Extensions in Windows 10:
- Clarity and Transparency: Displaying file extensions provides clarity to users by revealing the file types at a glance. This transparency helps users identify files accurately and avoid confusion, especially when dealing with similarly named files of different formats.
- Enhanced Security: File extensions can serve as indicators of potentially harmful files. Showing file extensions enables users to identify suspicious files, such as executable files masquerading as harmless documents, and exercise caution before opening them, thus enhancing security.
- Ease of File Management: Knowing the file types facilitates efficient file management. Users can organize, sort, and search for files more effectively based on their extensions, streamlining file management tasks and improving productivity.
- Compatibility and Interoperability: Understanding file types is essential for ensuring compatibility and interoperability across different applications and platforms. File extensions enable applications to recognize compatible file formats, facilitating seamless file sharing and collaboration.
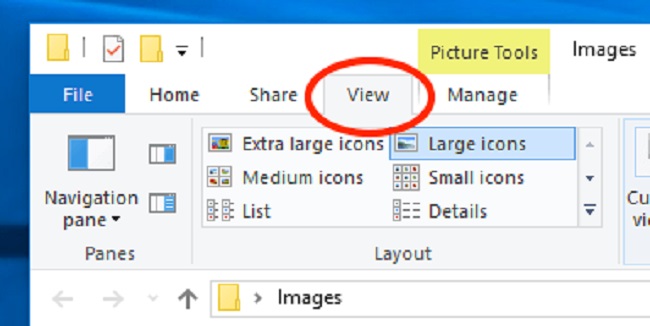
Displaying File Extensions in Windows 10 and Windows 11
Windows 10 and 11 share similar steps to display file extensions:
- Open ‘File Explorer’. You can do this by clicking on the folder icon on the taskbar or pressing ‘Win + E’.
- Click on the ‘View’ tab in the File Explorer menu.
- In the ‘Show/hide’ section, check the ‘File name extensions’ box.
Now, your file extensions will be visible in File Explorer.
Showing File Extensions in Windows 7
The process in Windows 7 is slightly different:
- Open ‘Windows Explorer’. You can do this by clicking on the folder icon on the taskbar.
- Click on ‘Organize’ in the top left corner.
- Choose ‘Folder and search options’.
- In the Folder Options window, go to the ‘View’ tab.
- Under ‘Advanced settings’, uncheck ‘Hide extensions for known file types’.
- Click ‘OK’.
File extensions should now be visible in Windows Explorer.
Displaying File Extensions via Registry Editor
For advanced users, the Windows Registry Editor offers another method to show file extensions. Before proceeding, remember that incorrect changes in the Registry Editor can cause significant problems, so proceed with caution:
- Press ‘Win + R’ to open the Run dialog box.
- Type ‘regedit’ and hit ‘Enter’.
- Navigate to
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced. - In the right pane, find ‘HideFileExt’. Double-click it and set its value data to ‘0’.
- Click ‘OK’ and close the Registry Editor.
Using PowerShell to Show File Extensions
If you prefer using command-line tools, PowerShell provides a way to show file extensions:
- Open PowerShell. You can do this by typing ‘PowerShell’ in the Start menu search bar and selecting ‘Windows PowerShell’.
- Enter the command
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced" -Name HideFileExt -Value 0. - Hit ‘Enter’.
This command changes the ‘HideFileExt’ registry key value to ‘0’, effectively enabling file extensions to be shown in File Explorer.
Understanding File Extensions
A file extension is a suffix added to the name of a computer file. It’s typically separated from the file name by a period. For instance, in ‘document.docx’, ‘docx’ is the file extension indicating that it’s a Microsoft Word document.
Read Also:
Conclusion
Showing file extensions in Windows enhances your visibility and control over your file system, whether you’re using Windows 7, 10, or 11.
Be it through the built-in File Explorer options, the Registry Editor, or PowerShell, these methods allow you to adapt your OS to your needs, giving you the reins to your digital experience.
As always, when dealing with system-level changes, proceed with caution and ensure you have a backup of your important data.


